Regional Geology
Metallogeny of Northern Chile
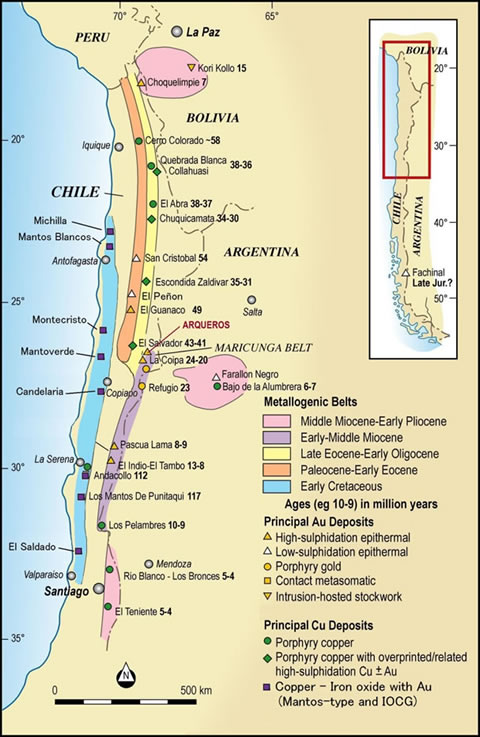
Northern Chile has four well-defined metallogenic belts which run parallel to the axis of the Andes. From youngest to oldest, these are:
- Upper Tertiary gold belt (El Indio & Maricunga sectors): located in the main Andean cordillera and characterised by high sulphidation epithermal and porphyry gold systems, including Esperanza, La Coipa, La Pepa, Marte-Lobo, Refugio and Cerro Casale- Aldebaran, of the Maricunga sector, and El Indio-Tambo and Pascua-Lama (formerly Nevada) of El Indio sector.
- Lower Tertiary gold belt: east of the coastal belt in the back-arc basin, and characterised by both low and high sulphidation epithermals, including San Cristobal, Guanaco and El Peñon gold and silver deposits.
- Lower Tertiary porphyry copper belt: located in the Precordillera (Domeyko Range) and parts of the main Andean Range, contains the giant Cu (Mo-Au) porphyries (El Teniente, Chuquicamata, Escondida, Zaldivar, Collahuasi, Los Pelambres, Los Bronces, Andina, and others). Controlled by Falla Oeste (West Fault), a ~3,000km long regional structural feature.
- Mesozoic Iron Oxide Copper-Gold belt (IOCG): located along the Coastal Ranges and parts of the Precordillera of Northern Chile. This is part of a Mesozoic volcanic arc characterised by Andean IOCG deposits, which include Los Colorados (Fe), El Algarrobo (Fe), El Romeral (Fe), Mantos Blancos (Cu-Ag), Mantoverde (Cu), Candelaria (Cu-Au-Fe), El Soldado (Cu) and Andacollo (Cu-Au) in Chile, and Marcona (Fe, Cu) in Peru.
Associated with many of the above are copper and gold-rich veins, supergene oxide-Cu and secondary-enriched sulphide and oxide copper blankets, skarns and exotica-type/Cu-cemented paleogravel deposits. Polymetallic Au-Ag vein and VMS deposits occur in the south of Chile.
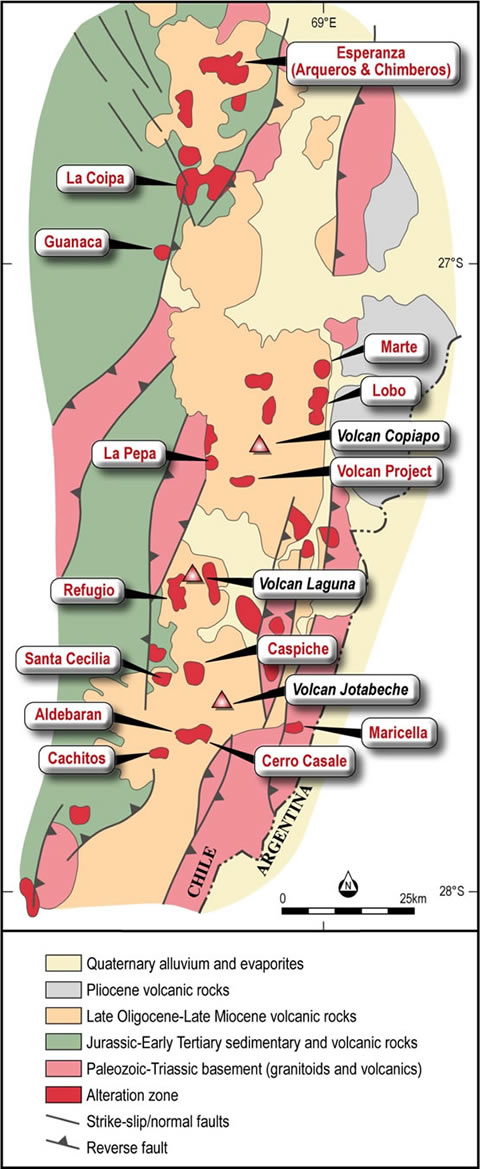
Arqueros is within the Esperanza-La Coipa sub-belt (Miocene age), located within the northern part of the Maricunga section of the Upper Tertiary gold belt.
Maricunga District
The Maricunga volcanic district is dominated by a series of Oligocene-Miocene volcanoes which extend for more than 200 km along the axis of the High Andes, or Altiplano, from Salar de Pedernales (26°S) to Cerro Pulido (28°S). The partially eroded volcanic edifices contain high sulphidation gold mineralized epithermal systems and porphyry gold and porphyry gold-copper deposits.
Volcanism from 26 to 6 Ma is represented by the deposition of calc-alkaline volcanics, diorite-gabbro intrusives, together with dacite domes, tuffs and breccias. These are superimposed by cycles of hydrothermal alteration.
The region is underlain by a Paleozoic basement of folded marine and terrestrial sediments (Devonian-Carboniferous) intruded by Pedernales Batholith (Permian) and overlain by Permo-Triassic acid volcanics, and Mesozoic andesitic volcanics, and marine and terrestrial sediments.
Deposits of the Maricunga Gold Belt
The mineral potential of the Maricunga gold belt was realized in the 1980s following an aggressive regional exploration, resulting in the discovery of a large number of mineralized zones. The period of late 1980s to mid-1990s saw the development of three mines: La Coipa, Refugio and Marte. To date over 90 million gold equivalent ounces have been placed in published resources since 1981.
Principal deposits of the Maricunga Gold Belt: Raw data sourced from published reports of Exeter Resource Corporation, Kinross Gold Corporation, Barrick Gold and Andina Minerals.
| Project | Type | Tonnes | Grade, g/t | % | Ounces (millions) | Tonnes | Status | |||
| Million | Gold | Silver | Copper | Gold | Silver | Gold equiv. | Copper (Million) |
|||
| La Coipa | HS | 70 | 1.4 | 82 | 3.2 | 185 | 6.2 | PRD | ||
| Chimberos | HS | 5 | 305 | 47 | 0.8 | CLD | ||||
| Arqueros | HS | 27 | 0.3 | 88 | 0.3 | 76 | 1.6 | EXP | ||
| Marte | PoAu | 46 | 1.4 | 2.1 | 2.1 | CLD/EXP | ||||
| Lobo | PoAu | 80 | 1.6 | 4.1 | 4.1 | PFS | ||||
| Volcan | PoAu | 529 | 0.6 | 10.6 | 10.6 | FS | ||||
| Refugio | PoAu | 244 | 0.8 | 6.3 | 6.3 | PRD | ||||
| Caspiche | PoAu | 1,473 | 0.5 | 1.3 | 0.20% | 24.3 | 60 | 25.3 | 2.7 | EXP |
| Cerro Casale | PoAu | 1,874 | 0.5 | 1.4 | 0.21% | 31.0 | 82 | 32.4 | 3.9 | FS |
| Total | 4,365 | 0.6 | 85 | 449 | 92 | 6.6* | ||||
Gold equivalence (AuEQ60) at Au/Ag price ratio of 60. HS = High Sulphidation PoAu = Porphyry Gold, PRD = Production, CLD = Closed, EXP = Exploration, PFS = Prefeasibility, FS = Feasibility
Maricunga-style gold mineralisation is characterised by low-grade bulk tonnage gold mineralisation hosted in porphyry gold deposits (+ copper) overlain by, or spatially associated with higher grade gold and silver mineralisation with high sulphidation epithermal characteristics.
In the La Coipa sector, from south of La Coipa mine to north of Esperanza, structural controls are N10-20E and N60-75W. Silver stratiform (“mantos”) deposits are emplaced in Paleozoic sedimentary strata (Chinches Formation) at La Coipa and Chimberos, and in Lower Miocene pyroclastics (Cerro Bravos Formation) at Arqueros. Metal-bearing solutions for silver mantos and structurally related vein-type gold mineralisation appear related to nearby dacite stocks.